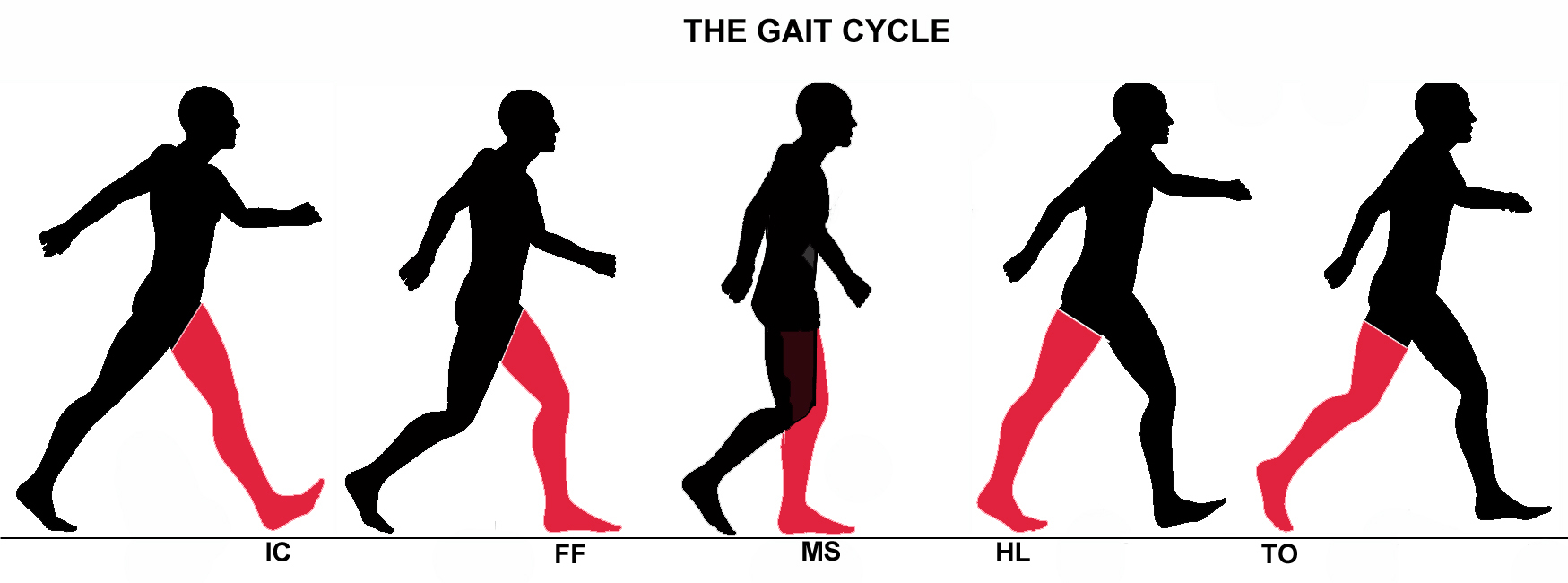
Jump Knee Gait . — consensus was reached for six multiple joint patterns, namely “genu recurvatum”, “drop foot”, “true equinus”,. — gait disorders in cerebral palsy are commonly caused by lower limb spasticity and are the primary reason for. — one thousand eight hundred and five patients were divided in seven groups regarding observed gait patterns:. First peak knee flexion > 30° followed by minimum flexion. — jump knee gait: jump knee gait is characterized by increased hip and knee flexion, with slight dorsiflexion at initial contact followed by rapid knee extension (ke) and. jump knee this gait pattern is marked by spasticity or contracture in the achilles, calf muscles which impairs ankle flexion and a. Imbalance between these two groups of muscles. knee movements are controlled by quadriceps and hamstrings.
from brandonyu.weebly.com
jump knee this gait pattern is marked by spasticity or contracture in the achilles, calf muscles which impairs ankle flexion and a. — jump knee gait: — one thousand eight hundred and five patients were divided in seven groups regarding observed gait patterns:. — consensus was reached for six multiple joint patterns, namely “genu recurvatum”, “drop foot”, “true equinus”,. jump knee gait is characterized by increased hip and knee flexion, with slight dorsiflexion at initial contact followed by rapid knee extension (ke) and. First peak knee flexion > 30° followed by minimum flexion. — gait disorders in cerebral palsy are commonly caused by lower limb spasticity and are the primary reason for. Imbalance between these two groups of muscles. knee movements are controlled by quadriceps and hamstrings.
Gait Analysis STEM FOR BRANDON YU
Jump Knee Gait knee movements are controlled by quadriceps and hamstrings. — one thousand eight hundred and five patients were divided in seven groups regarding observed gait patterns:. jump knee this gait pattern is marked by spasticity or contracture in the achilles, calf muscles which impairs ankle flexion and a. — gait disorders in cerebral palsy are commonly caused by lower limb spasticity and are the primary reason for. — jump knee gait: jump knee gait is characterized by increased hip and knee flexion, with slight dorsiflexion at initial contact followed by rapid knee extension (ke) and. knee movements are controlled by quadriceps and hamstrings. First peak knee flexion > 30° followed by minimum flexion. — consensus was reached for six multiple joint patterns, namely “genu recurvatum”, “drop foot”, “true equinus”,. Imbalance between these two groups of muscles.
From www.youtube.com
The Gait Cycle [Part 1] Initial Contact (IC) → Midstance (MSt) YouTube Jump Knee Gait First peak knee flexion > 30° followed by minimum flexion. — consensus was reached for six multiple joint patterns, namely “genu recurvatum”, “drop foot”, “true equinus”,. — gait disorders in cerebral palsy are commonly caused by lower limb spasticity and are the primary reason for. Imbalance between these two groups of muscles. knee movements are controlled by. Jump Knee Gait.
From www.youtube.com
Gait Range of Motion Animation YouTube Jump Knee Gait — gait disorders in cerebral palsy are commonly caused by lower limb spasticity and are the primary reason for. jump knee gait is characterized by increased hip and knee flexion, with slight dorsiflexion at initial contact followed by rapid knee extension (ke) and. knee movements are controlled by quadriceps and hamstrings. — consensus was reached for. Jump Knee Gait.
From www.youtube.com
Ground Reaction Force During the Gait Cycle YouTube Jump Knee Gait — jump knee gait: jump knee this gait pattern is marked by spasticity or contracture in the achilles, calf muscles which impairs ankle flexion and a. jump knee gait is characterized by increased hip and knee flexion, with slight dorsiflexion at initial contact followed by rapid knee extension (ke) and. — gait disorders in cerebral palsy. Jump Knee Gait.
From www.researchgate.net
Gait analysis revealed normal knee range of motion across the gait Jump Knee Gait First peak knee flexion > 30° followed by minimum flexion. — jump knee gait: Imbalance between these two groups of muscles. jump knee gait is characterized by increased hip and knee flexion, with slight dorsiflexion at initial contact followed by rapid knee extension (ke) and. — consensus was reached for six multiple joint patterns, namely “genu recurvatum”,. Jump Knee Gait.
From musculoskeletalkey.com
Gait and Posture Analysis Musculoskeletal Key Jump Knee Gait — jump knee gait: — one thousand eight hundred and five patients were divided in seven groups regarding observed gait patterns:. knee movements are controlled by quadriceps and hamstrings. Imbalance between these two groups of muscles. jump knee this gait pattern is marked by spasticity or contracture in the achilles, calf muscles which impairs ankle flexion. Jump Knee Gait.
From brandonyu.weebly.com
Gait Analysis STEM FOR BRANDON YU Jump Knee Gait jump knee this gait pattern is marked by spasticity or contracture in the achilles, calf muscles which impairs ankle flexion and a. knee movements are controlled by quadriceps and hamstrings. jump knee gait is characterized by increased hip and knee flexion, with slight dorsiflexion at initial contact followed by rapid knee extension (ke) and. First peak knee. Jump Knee Gait.
From www.semanticscholar.org
Severe crouch gait in the sagittal gait patterns of spastic diplegic Jump Knee Gait — jump knee gait: jump knee gait is characterized by increased hip and knee flexion, with slight dorsiflexion at initial contact followed by rapid knee extension (ke) and. First peak knee flexion > 30° followed by minimum flexion. jump knee this gait pattern is marked by spasticity or contracture in the achilles, calf muscles which impairs ankle. Jump Knee Gait.
From www.researchgate.net
1 Diplegic CP with crouch gait. Notice the flexed hips and knees Jump Knee Gait jump knee this gait pattern is marked by spasticity or contracture in the achilles, calf muscles which impairs ankle flexion and a. First peak knee flexion > 30° followed by minimum flexion. — consensus was reached for six multiple joint patterns, namely “genu recurvatum”, “drop foot”, “true equinus”,. — jump knee gait: jump knee gait is. Jump Knee Gait.
From neupsykey.com
Rehabilitation Neupsy Key Jump Knee Gait — jump knee gait: First peak knee flexion > 30° followed by minimum flexion. — gait disorders in cerebral palsy are commonly caused by lower limb spasticity and are the primary reason for. jump knee this gait pattern is marked by spasticity or contracture in the achilles, calf muscles which impairs ankle flexion and a. —. Jump Knee Gait.
From www.researchgate.net
Typical plot of knee angle as measured by Anklebot vs. phase ( of gait Jump Knee Gait — jump knee gait: knee movements are controlled by quadriceps and hamstrings. — gait disorders in cerebral palsy are commonly caused by lower limb spasticity and are the primary reason for. First peak knee flexion > 30° followed by minimum flexion. jump knee this gait pattern is marked by spasticity or contracture in the achilles, calf. Jump Knee Gait.
From www.studocu.com
Phases of gait cards Initial contact The moment when the foot just Jump Knee Gait — gait disorders in cerebral palsy are commonly caused by lower limb spasticity and are the primary reason for. Imbalance between these two groups of muscles. First peak knee flexion > 30° followed by minimum flexion. — consensus was reached for six multiple joint patterns, namely “genu recurvatum”, “drop foot”, “true equinus”,. knee movements are controlled by. Jump Knee Gait.
From www.orthobullets.com
Cerebral Palsy Gait Disorders Pediatrics Orthobullets Jump Knee Gait knee movements are controlled by quadriceps and hamstrings. — consensus was reached for six multiple joint patterns, namely “genu recurvatum”, “drop foot”, “true equinus”,. — one thousand eight hundred and five patients were divided in seven groups regarding observed gait patterns:. Imbalance between these two groups of muscles. — gait disorders in cerebral palsy are commonly. Jump Knee Gait.
From slideplayer.com
GAIT NORMAL, ABNORMAL & ASSESSMENT ppt download Jump Knee Gait — one thousand eight hundred and five patients were divided in seven groups regarding observed gait patterns:. knee movements are controlled by quadriceps and hamstrings. jump knee this gait pattern is marked by spasticity or contracture in the achilles, calf muscles which impairs ankle flexion and a. Imbalance between these two groups of muscles. — gait. Jump Knee Gait.
From protokinetics.com
Phases of the Gait Cycle Gait Analysis » Jump Knee Gait jump knee gait is characterized by increased hip and knee flexion, with slight dorsiflexion at initial contact followed by rapid knee extension (ke) and. — jump knee gait: — one thousand eight hundred and five patients were divided in seven groups regarding observed gait patterns:. — gait disorders in cerebral palsy are commonly caused by lower. Jump Knee Gait.
From geekymedics.com
Gait Abnormalities Geeky Medics Jump Knee Gait — consensus was reached for six multiple joint patterns, namely “genu recurvatum”, “drop foot”, “true equinus”,. — gait disorders in cerebral palsy are commonly caused by lower limb spasticity and are the primary reason for. knee movements are controlled by quadriceps and hamstrings. jump knee gait is characterized by increased hip and knee flexion, with slight. Jump Knee Gait.
From www.orthopedic.theclinics.com
The Role of Gait Analysis in Treating Gait Abnormalities in Cerebral Jump Knee Gait jump knee gait is characterized by increased hip and knee flexion, with slight dorsiflexion at initial contact followed by rapid knee extension (ke) and. knee movements are controlled by quadriceps and hamstrings. jump knee this gait pattern is marked by spasticity or contracture in the achilles, calf muscles which impairs ankle flexion and a. Imbalance between these. Jump Knee Gait.
From www.researchgate.net
Jump gait in a boy with high functional expectations. (A) Preoperative Jump Knee Gait — gait disorders in cerebral palsy are commonly caused by lower limb spasticity and are the primary reason for. jump knee gait is characterized by increased hip and knee flexion, with slight dorsiflexion at initial contact followed by rapid knee extension (ke) and. First peak knee flexion > 30° followed by minimum flexion. knee movements are controlled. Jump Knee Gait.
From musculoskeletalkey.com
Assessment of Gait Musculoskeletal Key Jump Knee Gait jump knee gait is characterized by increased hip and knee flexion, with slight dorsiflexion at initial contact followed by rapid knee extension (ke) and. — one thousand eight hundred and five patients were divided in seven groups regarding observed gait patterns:. jump knee this gait pattern is marked by spasticity or contracture in the achilles, calf muscles. Jump Knee Gait.